Things to know about UV-C and ozone
UV light
The sun brings it to light: UV light
History: As early as 1801, Johann Wilhelm Ritter observed in Jena that sunlight impairs the growth of mold fungi – the basis for today’s possibility of using UV-C rays to combat corona.
In 1877, two English researchers discovered that UV rays can apparently also reduce and even destroy other germs. Intensive research began. In 1902, the physician Dr. Gustav Kaiser in Berlin discovered that artificially produced UV radiation with quartz lamps promoted wound healing. The altitude sun was created to help heal and promote growth in children. Until the eighties, top athletes of the GDR were successfully treated with UV rays after operations for faster wound healing – including Kati Witt. So we are talking about an old, proven technique and not hocus-pocus.
What is UV light and how does it work?
- UV-C light with a wavelength of 254 nm modifies the DNA of a microorganism and thus stops reproduction
- If viruses or bacteria cannot reproduce, they die and are no longer infectious

Over the past 20 years, the use and technical application of UVC light has been continuously developed. new developments have been strongly advanced. Today, a wide range of safe applications is available.
These include
- Disinfection of air, surfaces and liquids (UVC radiation of wavelength 253.7 nm damages the DNA of microorganisms)
- Curing of UV sensitive paints, varnishes, potting compounds
- Ozone generation
- Artificial aging
- Analyses
- Material testing
- Fluorescence excitation
- Attractants (fly traps)
| 4 factors for UV-C disinfection – What is important? | UV-C light |
|---|---|
|
|
Ozone
Disinfection with ozone – What happens?
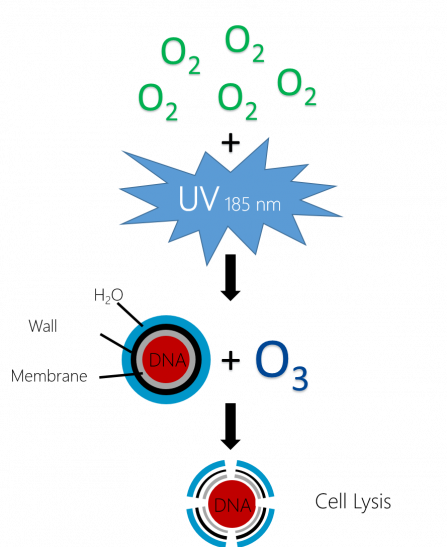
Ozone (O₃)
- is a natural cleaning agent that keeps the atmosphere clean
- Destroys the cell structure and can reach any place in a room as a gas
- has a half-life of about 40 minutes and is then automatically reduced to oxygen again
- is formed from oxygen to which energy from UV light with a wavelength of 185 nm is added
- breaks down and eliminates odors, bacteria, spores and viruses
4 factors for disinfection with ozone – What is important?
- Microorganism
- Concentration
- Time
- Environment